4.6 Temperature Measurement Systems
As a pharmacy technician, you may be asked to monitor the refrigerator and freezer temperatures of stored medications. For that reason, you need to have a good understanding of the two temperature scales used in pharmacy practice: the Fahrenheit temperature scale and the Celsius temperature scale. You must also be able to convert temperature readings between these two scales.
Understanding Temperature Measurement Systems
Daniel Fahrenheit, a German physicist, invented a temperature scale in 1724. The Fahrenheit temperature scale was based on ice water and salt as a low point (0° F) and the human body temperature as the high point (100° F). Fahrenheit used his own body temperature as the standard but, in the years that followed, scientists learned that body temperature varied. Therefore, the Fahrenheit scale was keyed to water for both the low point and the high point. The freezing point of water at sea level was set at 32° F, and the boiling point of water at sea level was set at 212° F.
In the early 1740s, Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, developed a thermometer with a difference of 100 degrees between freezing and boiling. Therefore, the Celsius temperature scale uses 0° C as the freezing point and 100° C as the boiling point. The Celsius temperature scale is commonly used in science as well as in healthcare settings.
Pharmacy technicians may be asked to help patients convert between temperature readings in degrees Celsius and degrees Fahrenheit. As with all conversions, this calculation must be done accurately.
Converting Celsius and Fahrenheit Temperatures
As mentioned earlier, you need to understand the conversions between Fahrenheit and Celsius temperature scales. The formulas for these conversions are based on the fact that each Celsius degree equals 1.8 or 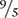 of each Fahrenheit degree. Below are the conversion formulas. Note that temperatures are rounded to the nearest tenth.
of each Fahrenheit degree. Below are the conversion formulas. Note that temperatures are rounded to the nearest tenth.
Degrees Celsius to Degrees Fahrenheit
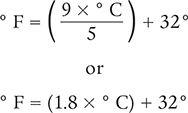
Degrees Fahrenheit to Degrees Celsius
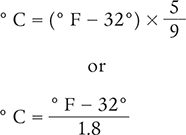
Example 4.6.1
Convert 40° C to its equivalent on the Fahrenheit temperature scale.
Solution 1
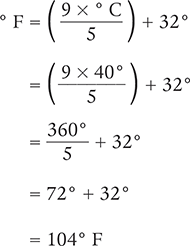
Solution 2
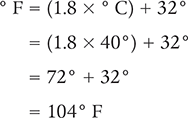
Answer: A temperature of 40° C is equivalent to 104° F.
Example 4.6.2
Convert 82° F to its equivalent on the Celsius temperature scale.
Solution 1
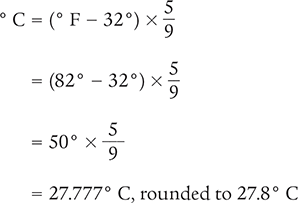
Solution 2
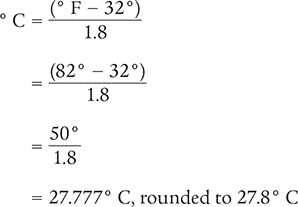
Answer: A temperature of 82° F is equivalent to 27.8° C.
Monitoring Temperature in Pharmacy Practice
Medications are required to be stored under specific temperature conditions. Some medications must be stored in refrigerated conditions, which are defined as being between 2° C and 5° C (35.6° F and 41° F). Other medications must be stored in frozen conditions. Freezers for medication storage should be maintained at temperatures between −25° C and −10° C (−13° F and 14° F). The storage of drugs outside of these recommended temperature parameters compromises the quality and safety of the medications.
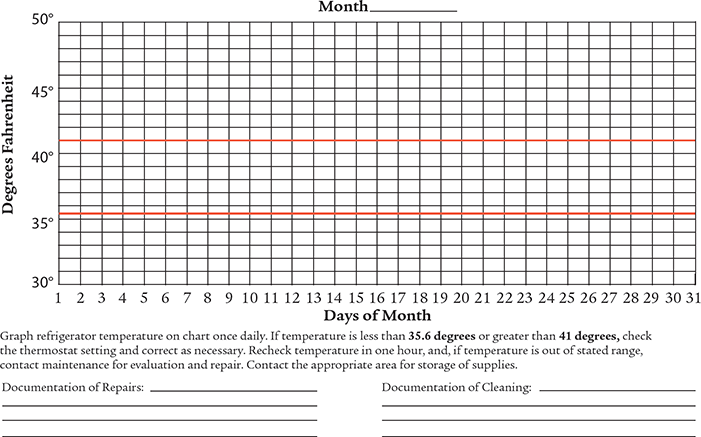
As mentioned earlier, you may be asked to monitor the pharmacy refrigerators and freezers for medication storage and to record these temperatures daily. Many pharmacies use specific charts for recording temperatures of refrigerators and freezers used for drug storage. See Figure 4.4 and Figure 4.5 for examples of the Celsius and Fahrenheit refrigerator temperature charts. To view examples of the freezer temperature charts for these two scales, see Figure 4.6 and Figure 4.7.
Figure 4.4 Drug Storage Refrigerator Temperature Chart (Celsius)
Figure 4.5 Drug Storage Refrigerator Temperature Chart (Fahrenheit)
Figure 4.6 Drug Storage Freezer Temperature Chart (Celsius)
Figure 4.7 Drug Storage Freezer Temperature Chart (Fahrenheit)
4.6 Problem Set
Convert the following Fahrenheit temperatures to Celsius. Round the temperatures to the nearest tenth of a degree.
0° F = ______________ ° C
23° F = _____________ ° C
36° F = _____________ ° C
40° F = _____________ ° C
64° F = _____________ ° C
72° F = _____________ ° C
98.6° F = ___________ ° C
100.5° F = __________ ° C
102.8° F = __________ ° C
105° F = ____________ ° C
Convert the following Celsius temperatures to Fahrenheit. Round the temperatures to the nearest tenth of a degree.
−15° C = ____________ ° F
18° C = _____________ ° F
27° C = _____________ ° F
31° C = _____________ ° F
38° C = _____________ ° F
40° C = _____________ ° F
49° C = _____________ ° F
63° C = _____________ ° F
99.8° C = ___________ ° F
101.4° C = __________ ° F
Applications
When making a mixture, you are instructed to heat the mixture to 130° C. You have only a Fahrenheit thermometer. What is the equivalent temperature on the Fahrenheit temperature scale?
Using the prescription below, answer the following questions.
 Alteplase Syringes
Alteplase SyringesAlteplase 2 mg/mL 50 mg
Sterile Water for Injection (SWFI) 25 mL
Reconstitute the alteplase with SWFI.
Draw up 5 mL in 10 mL syringes.
Label syringes with contents, concentration, and date of preparation.
Place syringes in freezer.

The syringes are stable for six months, or 180 days, at −20° C.
What is the Fahrenheit temperature at which you should store this product?
What beyond-use date should you put on this compound if today is February 1, 2025?
A compounding pharmacy is required to use dry heat sterilization for certain supply items. These items must undergo sterilization in a 300° F oven for 12 hours. At what Celsius temperature should the oven be set? Round the temperature to the nearest tenth of a degree.
Convert the following refrigerator temperatures and log them on the Celsius chart. Round the temperatures to the nearest tenth degree, and note any temperatures that fall outside the safe range.
Date
Degrees F
Degrees C
5/5
36.1°
a. _______
5/6
37.7°
b. _______
5/7
39.0°
c. _______
5/8
35.7°
d. _______
5/9
36.9°
e. _______
5/10
34.9°
f. _______
5/11
36.4°
g. _______
5/12
36.8°
h. _______
5/13
35.5°
i. _______
5/14
38.8°
j. _______
Convert the following refrigerator temperatures and log them on the Fahrenheit chart. Round the temperatures to the nearest tenth degree, and note any temperatures that fall outside the safe range.
Date
Degrees C
Degrees F
7/12
1.8°
a. _______
7/13
3.1°
b. _______
7/14
2.8°
c. _______
7/15
3.0°
d. _______
7/16
4.5°
e. _______
7/17
3.2°
f. _______
7/18
3.9°
g. _______
7/19
2.5°
h. _______
7/20
4.1°
i. _______
7/21
4.7°
j. _______